
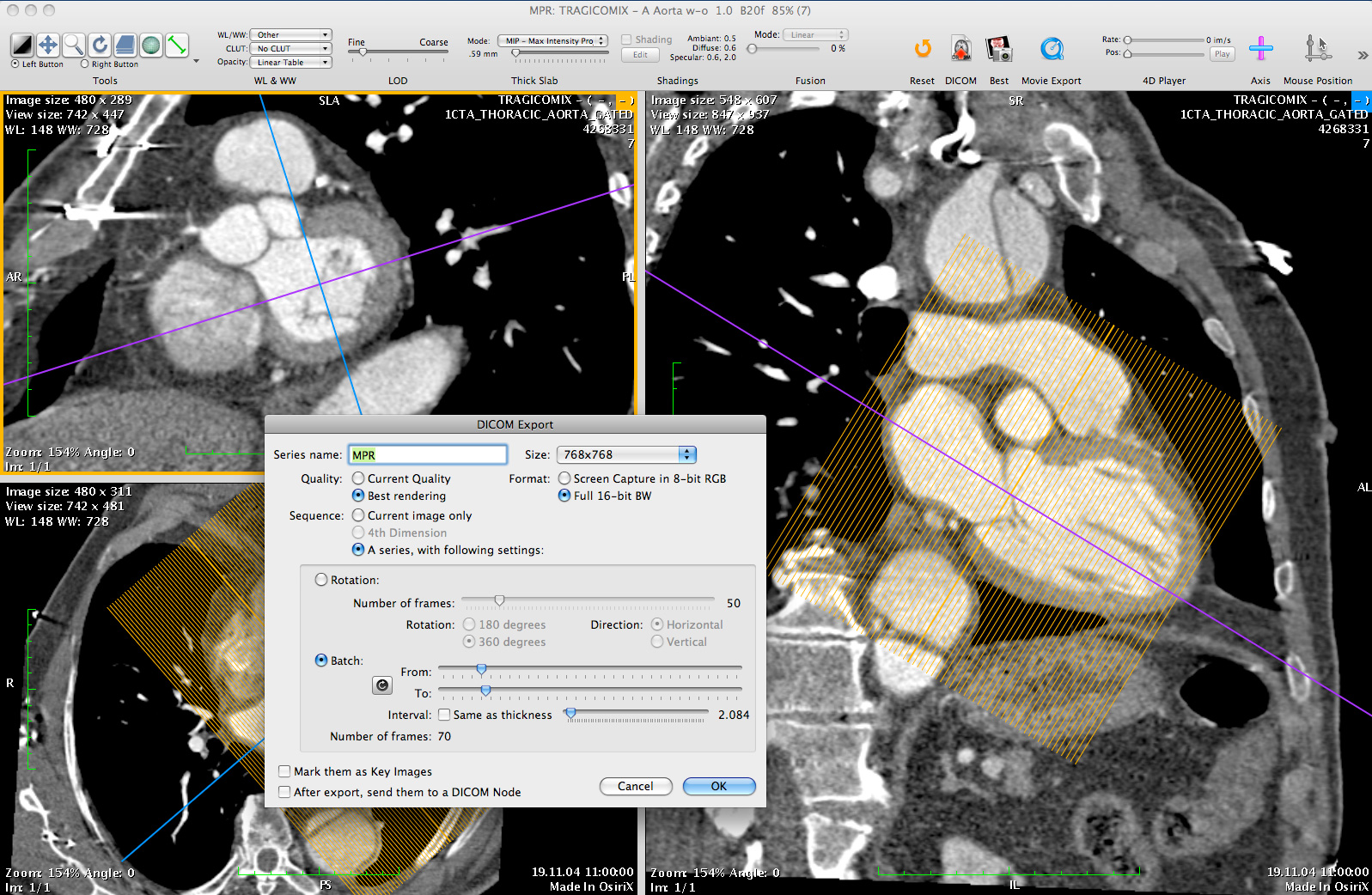
Position, Head-first Supine Matrix, 512 x 512. Protocol details are Tube voltage, 120 kvp Tube current, 67 mA Slice thickness, 1mm Slice distance, 0.8 mm Gantry tilt: 0° CT data acquisitionĬomputed tomography data was acquired on a 16-row multi-slice CT (Siemens Sensation 16, Siemens, Forchheim, Germany) using a high-resolution facial bone protocol for adult patients. Written consent was not obtained from participants for records usage, and clinical records were anonymized and de-identified prior to analysis. Due to the retrospective nature of the study, patient consent was not required after ethical committee approval of the study for both minors and adults. The study was approved by the Institutional Review Board of Chang Gung Memorial Hospital, Linkou Branch and adhered to ethical guidelines. Only patients older than 16 years old were included as this is the reported age for cessation of orbital volume increase. Exclusion criteria included underlying conditions such as congenital craniofacial malformations, cleft palate, thyroid diseases, previous orbital or eye surgery, and history of orthodontic or orthognathic surgery. All patients had received facial bone CT scans for evaluating craniofacial deformities other than conditions affecting the orbit, or trauma surveys with negative results. Only cases with bilateral normal orbits were included. The mean chronological age was 30☑2 years old (range 16 to 57). Twenty Taiwanese adults (10 male and 10 female) were randomly selected from the patients examined at Chang Gung Memorial Hospital, Linkou Branch between January and December, 2011. Finally, the inter-rater and intra-rater variability was compared to validate the accuracy of this tool through statistical analysis. In order to clarify the difference between two anterior limit definitions of orbital volume that exists in the literature, two different methods were compared using OsiriX software. A novel 3D-assisted methodology was used to perform calculations on orbital volume that provided a more intuitive method of evaluation for the non-radiologist. An open-source platform for personal computers, OsiriX, was used, with the second aim of establishing a convenient pre-operative planning process for individual surgeons.
#Osirix md fda software
One purpose of this study was to perform a leading volumetric analysis of normal orbits in Taiwanese adult patients using 3D imaging software based on CT data. However, the information obtained from normal population needs to be completed before executing volumetric assessments in diseased orbits.Īpparently, differences exist in orbital volume among ethnic groups, with there being insufficient information describing the normal orbital volume in Taiwanese adults. Apparently, the ability to accurately determine orbital volume could provide useful information in orbital reconstruction. CT volumetry was also assessed as a pre-operative planning tool to evaluate residual liver volume in hepatic carcinoma surgery.
For example, mastication muscle volume was evaluated by Analyze software to determine the influence of osseus mandible versus muscle in patients with square-face. 3D technologies such as volume/surface rendering and region-of-interest (ROI) based volume computations provide additional information to traditional 2D CT images. Recently, advancements in CT have led to images with higher resolution and less noise. Ĭomputed tomography (CT) based methodologies have been used since the 1980s to assist in formulating surgical plans with higher levels of accuracy. However, this often results in over or under-correction, and clinical experience demonstrates that globe position post-operatively is highly unpredictable. In the past, empirical assessments formed the basis of decision-making within the operating room. This should result in correction of globe position and assist in correcting visual manifestations such as diplopia. The principal goal of surgical intervention in trauma or congenital deformity is restoration of the bony anatomy of the orbital cavity. Noticeable manifestations of alterations in the orbital structure include physical signs and symptoms such as exophthalmos, enophthalmos, hypophthalmus, and diplopia.įor reconstructive plastic surgeons, the primary concern lies with the bony structure of the orbit.
congenital orbital dysplasia, Pfeiffer syndrome), and traumatic orbital fractures. sarcoidosis, Grave’s disease), congenital diseases (e.g. adenoid cystic carcinoma, retinoblastoma), inflammatory etiologies (e.g. The structure of the orbit can be influenced by various diseases, such as intraorbital tumors (e.g.

Quantitative determination of orbital volume is valuable to the evaluation and management of many conditions affecting the orbit.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
